Photovoltaics Array protection
When we talk about photovoltaic installations for voltage up to 1500V DC, we can mean different types of solutions and ways to implement them in reality. There are several ways to convert DC voltage to AC voltage.
| Anže Jerman Product manager |
1. Photovoltics 1500V d.c. systems
When we are talking about photovoltaic 1500V d.c. solar system, we could have in mind different types of solutions and how to implement them in reality. There exist several ways how to convert d.c. voltage to a.c.. The power conversion dictates us, how the system looks electrically, and what kind of protection we will need. In basic, photovoltaic systems could be divided by central and string inverter power conversion. Photovoltaic array protection is necessary for central inverter systems.
.
Figure 1: Photovoltaics 1500V Array protection
2. Photovoltaics Array protection
At the array level, DC string combiner boxes are connected together, protected with gPV fuse‑links. The nominal current of array protection depends on the output current of each DC combiner box. Nominal currents are in this case higher than in usual applications as solar systems could produce a high capacity of power. Because of that, NH fuse-links perfectly meet the solar system protection requirements. The output current of DC combiner boxes is usually in a range above 100A and up to 630A, depending on the size of the PV facility. Due to 1500V d.c. system voltage, fuse-links are developed in NHXL sizes.
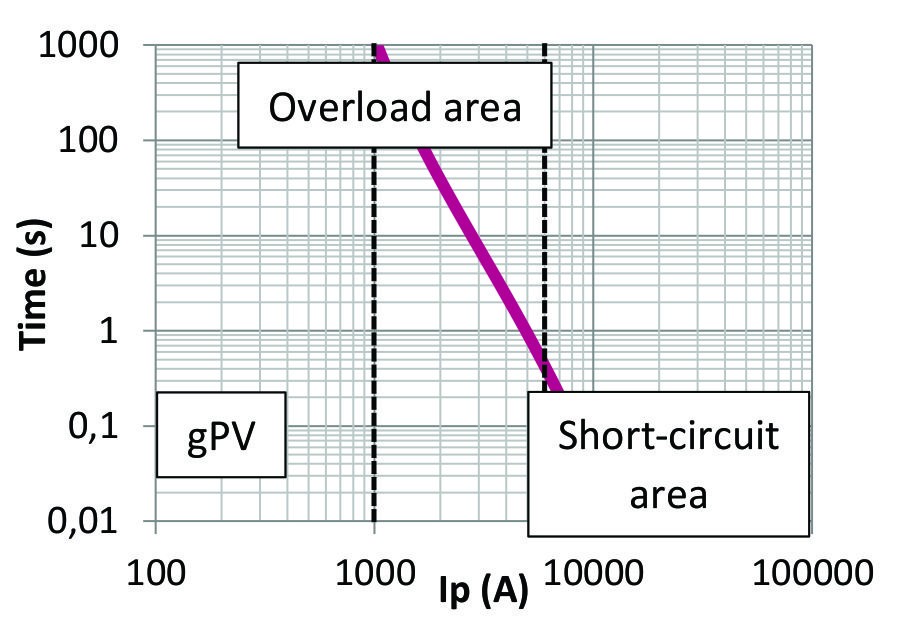
At the array level, the main protection belongs to d.c. cable systems. Protection needs to be designed to prevent damages in case of overloads or short-circuit currents. The gPV characteristic perfectly meets requirements, because of its fast operating in case of d.c. short-circuit and its full‑range characteristic which provides reliable protection to prevent unwanted damages which could be done in any area of I-t characteristic.
Full-range gPV characteristic is the perfect protection for d.c. photovoltaic cables. It covers overloads as a consequence of unpredicted overheating and short-circuits as a consequence of any failure in the PV system.
3. The example of PV Array protection
The example below shows, how to choose the right PV Array protection from the nominal current point of view. Chosen values are just informative to show an example.
Figure 2: The short-circuit current of PV Array is the sum of each short-circuit current of PV strings
The requirements for the design and protection of PV systems dictate International Electrotechnical Commission. Electrical norms for the designing and protection of PV systems are described in the IEC 62548 standard.
Determination of PV Array protection:
The first step to determining nominal current of PV Array protection is to find short-circuit current of PV modules, written on the backside of the PV module:
The short-circuit current of PV Array is the multiply of short-circuit current of PV module by a number of PV strings.
The nominal current of PV Array protection is according to the calculation between 144A and 276A.
In the example are not included other outdoor conditions (ambient temperature...). The nominal current of Array protection should be recalculated according to the complete information about the environmental conditions of the installation.
4. Conclusions
The protection of PV Arrays in central inverter systems is necessary. The main function of Array protection is to protect d.c. cable systems, against damages as a consequence of overloads and short‑circuit currents. Full-range gPV characteristic provides reliable protection. Its fast operation and a wide area of protection perfectly meet PV system requirements.
From the calculation above, we can see, that the range of protection is quite wide. The job for electrical designers is to choose suitable nominal current, according to the available technical information provided for a specific solar project.